Slot Waveguide
Slot displacement from the centreline of the width of the waveguide to the center of the slot, specified as a real-valued scalar or vector in meters. Note If SlotOffset is a vector, it can be the size of 1-by. A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. A slotted waveguide is a waveguide that is used as an antenna in microwave radar applications. When the plate is driven as an antenna by a driving frequency, the slot radiates electromagnetic waves in a way similar to a dipole antenna.The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving.
- Journal of the Optical Society of America B
- Vol. 29,
- Issue 6,
- pp. 1490-1496
- (2012)
- •https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.29.001490
- Share
- Get CitationCopy Citation TextZhaolin Lu and Wangshi Zhao, 'Nanoscale electro-optic modulators based on graphene-slot waveguides,' J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1490-1496 (2012)Export Citation
Abstract
Research on graphene has revealed its remarkable electro-optic properties, which promise to satisfy the needs of future electro-optic modulators. However, its ultrasmall thickness, compared with operating light wavelength, downplays its role in an optoelectronic device. The key to achieve efficient electro-optic modulation based on graphene is to enhance its interaction with light. To this end, some novel waveguides and platforms will be employed to enhance the interaction. Herein, we present our recent exploration of graphene electro-optic modulators based on graphene sandwiched in dielectric or plasmonic waveguides. With a suitable gate voltage, the dielectric constant of graphene can be tuned to be very small due to the effect of intraband electronic transition, resulting in “graphene-slot waveguides” and greatly enhanced absorption modes. Up to 3 dB modulation depth can be achieved within 800 nm long silicon waveguides, or 120 nm long plasmonic waveguides based on three-dimensional numerical simulations. They have the advantages of nanoscale footprints, small insertion loss, low power consumption, and potentially ultrahigh speed, as well as being CMOS-compatible.
©2012 Optical Society of America
Full Article PDF ArticleOSA Recommended Articles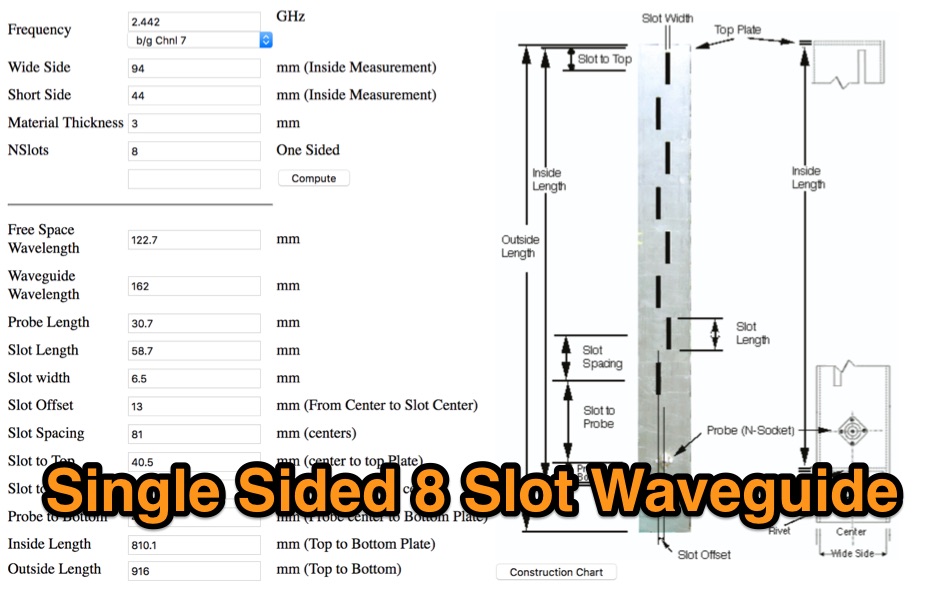 Design of a graphene-based dual-slot hybrid plasmonic electro-absorption modulator with high-modulation efficiency and broad optical bandwidth for on-chip communication
Design of a graphene-based dual-slot hybrid plasmonic electro-absorption modulator with high-modulation efficiency and broad optical bandwidth for on-chip communicationZhongwei Wu and Yin Xu
Appl. Opt. 57(12) 3260-3267 (2018)
Abhijeet Phatak, Zhenzhou Cheng, Changyuan Qin, and Keisuke Goda
Opt. Lett. 41(11) 2501-2504 (2016)
Chao Xu, Yichang Jin, Longzhi Yang, Jianyi Yang, and Xiaoqing Jiang
Opt. Express 20(20) 22398-22405 (2012)
References
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Citation lists with outbound citation links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Cited By
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Cited by links are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Slot Resonator Wall
Figures (5)
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Figure files are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
Metrics
You do not have subscription access to this journal. Article level metrics are available to subscribers only. You may subscribe either as an OSA member, or as an authorized user of your institution.
Contact your librarian or system administrator
or
Login to access OSA Member Subscription
The model analyses the mode propagation within a nano slot waveguide. In a slot waveguide configuration, two high refractive index slabs (~3.48) are placed adjacent to the low refractive index slot (~1.44). Mode analysis was performed on a 2D cross section of a slot waveguide for an operating wavelength of 1.55[um]. Further analysis was carried out to optimize the width of the slot to deliver maximum optical power and optical intensity through the slot area.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
Slot Waveguide Antenna
- COMSOL Multiphysics®and
Slot Resonator
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.